Database / SQL
One of the ways is to use correlated subquery to find the Nth highest salary as shown below.
SELECT name, salary FROM employee emp1 WHERE N-1 = (SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT salary) FROM Employee emp2 WHERE emp2.salary > emp1.salary)
In the above query, the 'N' may be replaced with 2 to find the second highest salary. Also for the top 2 salaries, replace the condition N-1= with N-1>=.
RANK generates the ranking within your ordered partition. Ties are assigned the same rank, with the next ranking(s) skipped. So, if you have 2 items at rank 2, the next rank listed would be ranked 4.
DENSE_RANK again gives you the ranking within your ordered partition, but the ranks are consecutive. No ranks are skipped even if there are ranks with multiple items.
NULLS are ordered at LAST for ascending order, and NULLS are ordered FIRST in case of descending order.
Extend the order by clause to include an optional NULLS FIRST or NULLS LAST clauses as shown below.
SELECT * FROM Employee ORDER BY dept_id ASC NULLS FIRST; SELECT * FROM Employee ORDER BY dept_id DESC NULLS LAST;
ROWID is the physical location of a row. It is the fastest way of locating a row, faster even than a primary key lookup. So it could be useful in certain types of transaction where we select some rows, store their ROWIDs and then later on use the ROWIDs in where clauses for DML against those same rows.
The Oracle SELECT ... FOR UPDATE syntax implicitly uses ROWID, when we update the locked row using WHERE CURRENT OF. Also the EXCEPTIONS table (referenced when applying constraints with the EXCEPTIONS INTO clause) has a column ROW_ID. This allows us to quickly identify the rows which are breaking our constraint.
For each row returned by a query, the ROWNUM pseudocolumn returns a number indicating the order in which Oracle selects the row from a table or set of joined rows. The first row selected has a ROWNUM of 1, the second has 2, and so on.
You can use ROWNUM to limit the number of rows returned by a query, as in this example:
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE ROWNUM < 10;
If an ORDER BY clause follows ROWNUM in the same query, then the rows will be reordered by the ORDER BY clause. The results can vary depending on the way the rows are accessed.
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE ROWNUM < 11 ORDER BY dept;
If you embed the ORDER BY clause in a subquery and place the ROWNUM condition in the top-level query, then you can force the ROWNUM condition to be applied after the ordering of the rows. For example, the following query returns the employees with the 10 smallest employee numbers. This is sometimes referred to as top-N reporting:
SELECT * FROM (SELECT * FROM employees ORDER BY dept) WHERE ROWNUM < 11;
In a SQL database query, a correlated subquery (also known as a synchronized subquery) is a subquery (a query nested inside another query) that uses values from the outer query. Because the subquery is evaluated once for each row processed by the outer query, it can be inefficient.
The ratio of distinct values to the number of table rows. A column with only two distinct values in a million-row table would have low cardinality.
To view the index cardinality, you use the SHOW INDEXES command.
A placeholder in a SQL statement that must be replaced with a valid value or value address for the statement to execute successfully.
By using bind variables, you can write a SQL statement that accepts inputs or parameters at run time. The following example shows a query that uses v_empid as a bind variable:
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id = :v_empid;
An index organized like an upside-down tree. A B-tree index has two types of blocks: branch blocks for searching and leaf blocks that store values. The leaf blocks contain every indexed data value and a corresponding rowid used to locate the actual row. The "B" stands for "balanced" because all leaf blocks automatically stay at the same depth.
The clustered index is used to reorder the physical order of the table and search based on the key values. A table can have only one clustered index.
NonClustered Index does not alter the physical order of the table and maintains logical order of data. A table can have 999 non-clustered indexes.
Indexes are schema objects that are logically and physically independent of the data in the objects with which they are associated. Thus, an index can be dropped or created without physically affecting the table for the index.
A composite index, also called a concatenated index, is an index on multiple columns in a table. Columns in a composite index should appear in the order that makes the most sense for the queries that will retrieve data and need not be adjacent in the table.
Composite indexes can speed retrieval of data for SELECT statements in which the WHERE clause references all or the leading portion of the columns in the composite index.
Self join is often very useful to convert a hierarchical structure to a flat structure. It is used to join a table to itself as like if that is the second table.
ACID is a set of properties that you would like to apply when modifying a database.
- Atomicity,
- Consistency,
- Isolation,
- Durability.
Atomicity means that you can guarantee that all of a transaction happens, or none of it does; you can do complex operations as one single unit, all or nothing, and a crash, power failure, error, or anything else won't allow you to be in a state in which only some of the related changes have happened.
Consistency means that you guarantee that your data will be consistent; none of the constraints you have on related data will ever be violated.
Isolation means that one transaction cannot read data from another transaction that is not yet completed. If two transactions are executing concurrently, each one will see the world as if they were executing sequentially, and if one needs to read data that is written by another, it will have to wait until the other is finished.
Durability means that once a transaction is complete, it is guaranteed that all of the changes have been recorded to a durable medium (such as a hard disk), and the fact that the transaction has been completed is likewise recorded.
Candidate key is a super key from which you cannot remove any fields.
A super key is any combination of columns that uniquely identifies a row in a table.
There is NO GO statement in MySQL. Semicolon (;) at the end of each line works as GO statement in MySQL.
INSERT INTO myTable (ID) values (14);
- INNER JOIN,
- LEFT JOIN,
- RIGHT JOIN,
- OUTER JOIN,
- LEFT JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOIN,
- RIGHT JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOIN,
- OUTER JOIN EXCLUDING INNER JOIN.
The SQL CROSS JOIN produces a result set which is the number of rows in the first table multiplied by the number of rows in the second table, assuming no 'where' clause is used along with CROSS JOIN. This kind of result is also called as Cartesian Product. If, WHERE clause is used with CROSS JOIN, it functions like an INNER JOIN.
SELECT table112.id,table112.bval1,table112.bval2, table111.id,table111.aval1 FROM table112 CROSS JOIN table111;
The SQL SELF JOIN is used to join a table to itself as if the table were two tables, by renaming at least one table with alias in the SQL statement.
Primary key doesn't allow null while unique key allow null.
Views are virtual and the query is executed every time it is accessed. The upside of a view is that it will always return the latest data to you. The downside of a view is that its performance depends on how good a select statement the view is based on. If the select statement used by the view joins many tables, or uses joins based on non-indexed columns, the view could perform poorly.
Materialized views are disk-based and are updated periodically based upon the query definition.
Using the show global status command we can determine the number of selects, updates since the last database restart. To find per day run the command now and after 24 hours and subtract the last count with the latest.
#For select SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Com_select'; #For update SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Com_update';
For INSERT and DELETE replace the query with 'Com_insert' ,'Com_delete' respectively.
Indexes may slow down inserts, deletes and updates due to locking and also costs disk space.
- Faster query execution,
- quick data retrieval,
- facilitates sorting and thus eliminate post fetch sorting strategy,
- Unique indexes uniquely identifies records in the database.
There are 2 main types.
Clustered indexes define the physical sorting of a database table rows in the storage media. Each table may have only one clustered index.
Non-clustered indexes are created outside of the database table and contain a sorted list of references to the table itself.
No. A view and table cannot have same name.
To find the second largest, Use the max aggregate function to find the largest and filter the largest value and find the maximum value again that yields the second largest.
SELECT MAX( column) FROM table WHERE column< ( SELECT MAX( column) FROM table )
Hi there, my suggestion would be using a DB sequence (or a separate table for the sequence in MYSQL DB) to generate a unique number (for example,456) and have a Database trigger (before-insert) to prefix "TCS-". This way we will make sure a unique id is generated. This solution completely relies on database objects.
if we want to achieve this using Java/hibernate, we can generate a unique number and prefix "TCS-".
DELETE is a DML statement that deletes complete rows from the table and produces the count of deleted rows. It also allows us to filter and delete any specific records using the WHERE clause from the table. After executing this command, we can rollback the deleted data because it makes an entry in the transaction log for each deleted row.
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
TRUNCATE is a DDL statement used to remove complete data from the table without removing the table structure. So indexes, constraints, columns, the structure is maintained even after the statement is executed. We cannot use the WHERE clause with this command so that filtering of records is not possible. After executing this command, we cannot rollback the deleted data because the log is not maintained while performing this operation.
The truncate command deallocates the pages instead of rows and makes an entry for the deallocating pages instead of rows in transaction logs. This command locks the pages instead of rows; thus, it requires fewer locks and resources. Note that we cannot use the truncate statement when a table is referenced by a foreign key or participates in an indexed view.
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;
Option 1: WITH RANK_SALARY AS ( SELECT *, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY Salary Desc) AS SALARY_RANK FROM Employees ) SELECT Name, Salary FROM RANK_SALARY WHERE SALARY_RANK = 2 Option 2: SELECT Salary FROM Employees ORDER BY Salary DESC LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1
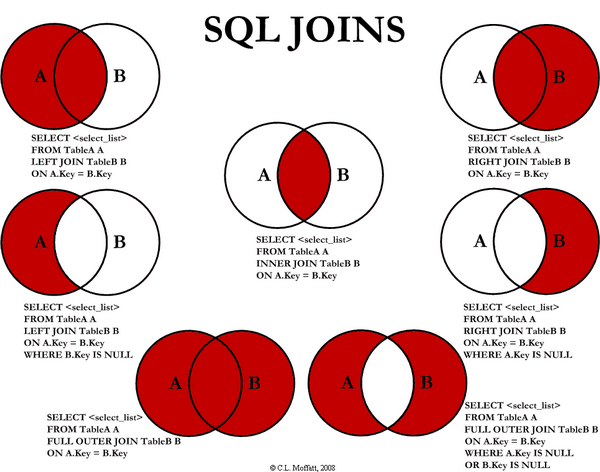
There are different types of joins available in SQL:
LEFT JOIN: returns all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table.
RIGHT JOIN: returns all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table.
FULL JOIN: combines the results of both left and right outer joins.
The joined table will contain all records from both the tables and fill in NULLs for missing matches on either side.SELF JOIN: joins a table to itself as if the table were two tables, temporarily renaming at least one table in the SQL statement.
CARTESIAN JOIN: returns the Cartesian product of the sets of records from the two or more joined tables.
SQL queries can be categories into 4 main Categories:
DDL (Data Definition Language).
As the name suggests, these types of queries are used to define the structure of data. Like the structure of a table, schema and modify it. Example,
- CREATE: This command is used to create tables, database, schema etc.
- DROP: This command is used to drop tables and other database objects.
- ALTER: This command is used to alter the definition of database objects.
- TRUNCATE: This command is used to remove tables, procedures, views, and other database objects.
- ADD COLUMN: This command is used to add any column to the table schema.
- DROP COLUMN: This command is used to drop a column from any table structure.
DML (Data Manipulation Language)
This type of queries is used to manipulate data in the database. Example,
- SELECT INTO: This command is used to select data from one table and insert it into another table.
- INSERT: This command is used to insert data/records into a table.
- DELETE: This command is used to delete records from the table.
- UPDATE: This command is used to update the value of any record in the database.
DCL (Data Control Language)
This category of SQL queries deals with the access rights and permission control of the database. Example,
- GRANT: This command is used to grant access rights to database objects.
- REVOKE: This command is used to withdraw permission from database objects.
TCL (Transaction Control Language)
The transaction is a set of commands that perform a specific task on objects in a single unit of execution. So TCL commands deals with transactions in a database. Example,
- COMMIT: This command is used to commit a transaction. Once committed, it cannot be rolled back. This means the previous image of the database before running this transaction cannot be retrieved.
- ROLLBACK: Rollback is used to revert the steps in transactions if an error occurs. SAVEPOINT: This command sets a savepoint in the transaction to which steps can be rolled back.
- SET TRANSACTION: This command is used to set the characteristics of the transaction.
SQL Constraints are the guidelines used to create restrictions to be implemented on the contents of the table or database so that the records should obey these rules in order to be placed in that table. Some of the constraints are NOT NULL, CHECK, UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY, DEFAULT.
You can get the third-highest salary by using limit, by using TOP keyword and sub-query. TOP works with MS SQL server and LIMIT works with MySQL.
TOP keyword:
SELECT TOP 1 salary
FROM
(SELECT TOP 3 salary
FROM Table_Name
ORDER BY salary DESC) AS Comp
ORDER BY salary ASC
limit:
SELECT salary
FROM Table_Name
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 2, 1
by subquery:
SELECT salary
FROM
(SELECT salary
FROM Table_Name
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 3) AS Comp
ORDER BY salary
LIMIT 1;
Terminate the query with \G in place of ;. For example:
SELECT * FROM sometable\G
select e1.emp_name, e1.mgr_name, e1.emp_salary from Employee e1, (select mgr_name, max(emp_salary) empMaxSalary from Employee group by mgr_name ) e2 where e1.mgr_name = e2.mgr_name and e1.emp_salary = e2.empMaxSalary
